DTP Branches and Offices
Milestone (1957, 1967)

The first hard-disk drive, IBM’s RAMAC 305 stored 5 million characters on 50 24-inch disks.

The RAMAC 305 system. Courtesy of EE Times Online. 8 July 1998.
Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS)
The 12-year period from 1955 to 1967 saw the acquisition and testing of over 114,000 synthetic and pure natural products. The compounds were identified and tracked by their National Service Center (NSC) numbers, a term which has escaped "reorganization" over the years. Compound records, including the identity of the supplier, structural information, quantities, and shipping histories for each compound, were kept on paper chemistry cards.
Screening results for compounds had been maintained on computer since 1957. The state-of-the-art computer at the time was an IBM 305 (RAMAC), the first of its kind with a magnetic disk drive. The drive consisted of 50 24-inch discs that collectively could hold 5 million characters of information, which translates to about 4.4 MB. The computer and drive weighed in at 2000 pounds, and the rental cost of the drive alone was $35,000 per year. In today's dollars, that is the equivalent of having to pay $238,000 for less than 1% of the capacity of a modern compact disc! Paper output from the RAMAC was sent to Bethesda and kept in large binders; updating and retrieving data from these binders was a manual task.
In 1967, the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) was awarded a contract to computerize the chemical records, eliminating the need to update the chemistry cards. The signing of the National Cancer Act of 1971 gave the NCI unique autonomy within NIH with special budgetary authority, and for the CCNSC it increased the effort to acquire new compounds for testing with the awarding of an acquisition and inventory contract responsible for the collection and documentation of test agents.
In 1985, a contract effort to develop an electronic database eliminated the need to hand-draw structures. DTP now had an in-house Drug Information System (DIS) that allowed the transfer of input activities from CAS to the acquisition contractor and gave the staff the capacity to perform interactive searches of structural, inventory, and shipment information.
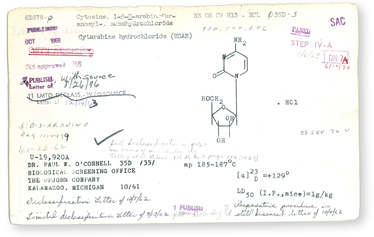
A paper chemistry card created in 1961 for cytarabine hydrochloride. Courtesy of DTP.





